
94% of Mobile Internet Users in Iran Rely on 4G; 5G Adoption Remains at 2%
Iran's mobile internet market thrives, with 94% on 4G. However, 5G adoption lags at 2%, and fiber-optic expansion progresses slowly.
The latest quarterly report released by the Communication Regulatory Authority of Iran highlights significant developments in the country’s telecommunications sector during the spring of 2025. The mobile internet market continues to drive growth, while fixed-line telephony faces a steady decline in subscribers. Key takeaways from the report include heavy reliance on 4G technology, the limited adoption of 5G, and the slow expansion of fiber-optic internet.
According to the report, the number of active mobile subscribers in Iran reached 164.19 million by the end of June 2025, reflecting a 6.05% growth compared to the same period last year. Meanwhile, mobile broadband users increased by 6.41% to 121.25 million, while fixed-line subscriptions declined by 2.34%. Fixed broadband services experienced only a modest 1.47% increase, with subscribers growing from 11.10 million to 11.27 million.
Mobile Operator Market Share
Hamrah-e-Aval (MCI) continues to dominate the mobile market with over 88 million active subscribers, securing a 54% market share. It is followed by Irancell with 69 million users (42%) and Rightel with 5.7 million subscribers (3.52%).
The report reveals that MCI’s total allocated lines (HLR) reached 105.36 million, with 88.74 million active lines, giving it a precise market share of 54.04%. This marks a slight increase of 0.05% from the previous period. In contrast, Irancell’s market share decreased by 0.04%, while Rightel experienced a 0.01% decline.
5G: Far from Mainstream
The penetration rate for mobile subscriptions rose by 5.31% to 189.68%, with over 94% of mobile internet users relying on 4G networks. In stark contrast, 5G accounts for only 2% of the user base, indicating that the technology is far from widespread adoption and remains constrained to limited coverage.
In terms of 5G site deployment, MCI leads with 1,227 active sites, followed by Irancell with 1,153 sites, underscoring a competitive race in next-generation infrastructure.
MCI Leads Mobile Broadband Growth
The report also highlights MCI’s continued dominance in mobile broadband, capturing a 54% market share, followed by Irancell at 42% and Rightel at 4%. In terms of network performance, MCI delivered an average download speed of 16.2 Mbps on 4G, while Irancell and Rightel recorded 12.46 Mbps and 20.18 Mbps, respectively. Data service success rates for all operators exceeded 99.5%, although the quarter saw 9,765 complaints about mobile services and 25,865 complaints about fixed-line services, primarily concerning connectivity issues and service outages.
For 4G networks, MCI boasts a 99.68% data service success rate, marginally outperforming Irancell (99.56%) and Rightel (99.61%). For 3G, Irancell leads with a 97.71% success rate, followed by Rightel (98.94%) and MCI (99.38%).
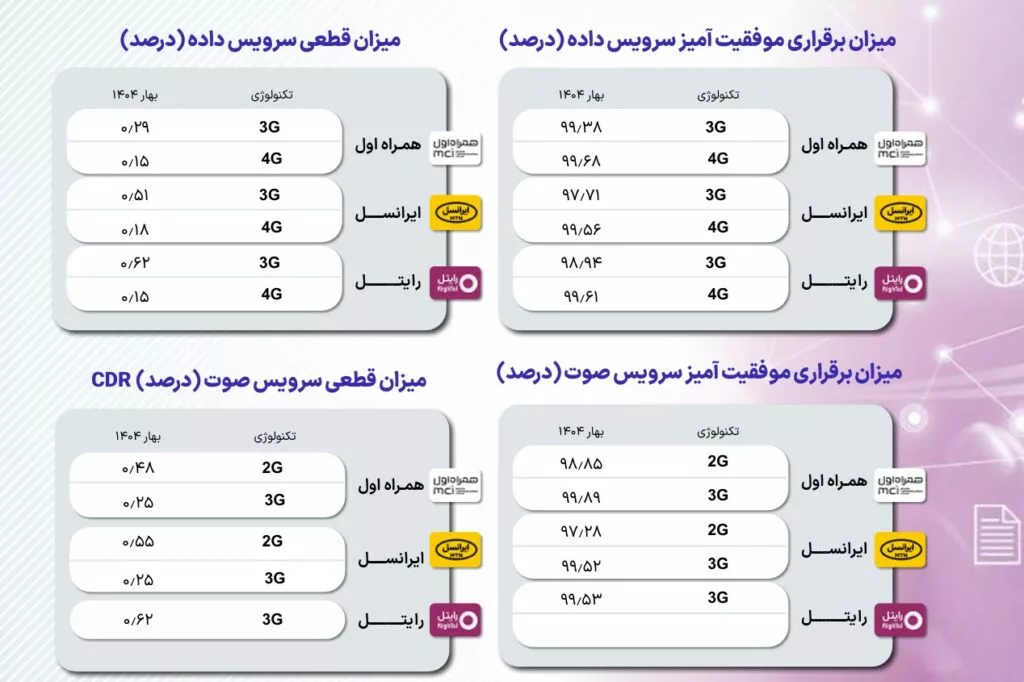
Voice and Messaging Trends
Total voice traffic in the mobile network surpassed 86 billion minutes in spring 2025, marking a 3.46% increase from the previous year. MCI accounted for 68% of this traffic, while Irancell and Rightel captured 31% and 1%, respectively. However, the average monthly call duration per user declined by 2.44%, dropping to 174.79 minutes from 179 minutes last year.
Text messaging also remained significant, with over 56 billion messages sent during the quarter. The average user sent 114.13 messages per month. MCI retained a 54% share of the messaging market, followed by Irancell (40%) and Rightel (6%).
The Gradual Decline of Fixed-Line Telephony
In the fixed-line sector, the total number of operational lines dropped to 23.59 million, a 0.73% decrease from last year. With a penetration rate of 32.32%, the decline is attributed to shifting communication habits, the rise of internet-based voice calls, and underinvestment in traditional infrastructure.
Fiber-Optic Internet: A Slow Rollout
Fixed broadband services, despite slight growth, continue to face development challenges. The number of subscribers reached 11.27 million, representing a 1.47% increase. xDSL technology dominates with 7.6 million subscriptions, followed by TD-LTE (2.55 million), fiber-optic (691,000), and public Wi-Fi networks (387,000). These figures highlight the limited penetration of fiber-optic technology and its sluggish rollout.
Conclusion: Gaps in Modernization
While Iran's mobile communications sector demonstrates consistent growth and broad coverage, the adoption of advanced technologies, such as 5G and fibre-optic internet, remains slow and insufficient to meet modern demands. Fixed-line telephony continues its downward trajectory, and without strategic policy adjustments and investments, this decline may accelerate. Furthermore, despite relatively good mobile internet quality, disparities in service speed and coverage between urban and rural areas persist, posing a challenge that requires concerted efforts from both the government and operators.










